Pruning Pepper Plants: A Comprehensive Guide to Maximizing Health and Yield
Pruning your pepper plants may seem counterintuitive, but it’s a crucial technique to enhance their health and productivity. Proper pruning encourages robust growth, improves air circulation, and boosts fruit quality. This guide will help you understand when and how to prune your pepper plants for optimal results.
Why Prune Pepper Plants?
1. Enhanced Air Circulation
- Benefit: Pruning improves air flow around the plant, which helps reduce the risk of fungal diseases. Better air circulation allows leaves to dry more quickly after watering or rainfall, minimizing disease risk.
2. Increased Sunlight Penetration
- Benefit: Removing excess foliage lets sunlight reach the inner parts of the plant, enhancing photosynthesis. This leads to better overall growth and energy production.
3. Encouraged Bushier Growth
- Benefit: Pruning promotes bushier growth instead of tall, leggy plants. A bushier plant with more branches can produce more flowers and, consequently, more peppers.
4. Better Fruit Quality
- Benefit: Focusing the plant’s energy on fewer, more developed fruits rather than excessive foliage results in larger, healthier peppers with better flavor and texture.
When to Prune Pepper Plants
1. Early Growth Stage
- Timing: Prune when the plant is about 6-8 inches tall and has at least 4-6 true leaves. Early pruning helps shape the plant and establish a strong base for future growth.
2. After the First Fruits Set
- Timing: Lightly prune after the first set of fruits forms to redirect energy from foliage to fruit development. Be careful not to over-prune, as the plant needs leaves for photosynthesis.
3. Mid to Late Growing Season
- Timing: Perform light pruning to remove damaged, diseased, or overcrowded branches. This keeps the plant healthy and productive throughout the season.
4. Before the End of the Season
- Timing: About a month before the first frost, top off the plants to stop new flower production and focus on ripening existing fruits.
How to Prune Pepper Plants
1. Gather Your Tools
- Tools Needed:
- Sharp pruning shears or scissors
- Gloves for hand protection
- Disinfectant (e.g., rubbing alcohol) to sterilize tools
2. Early Pruning Steps
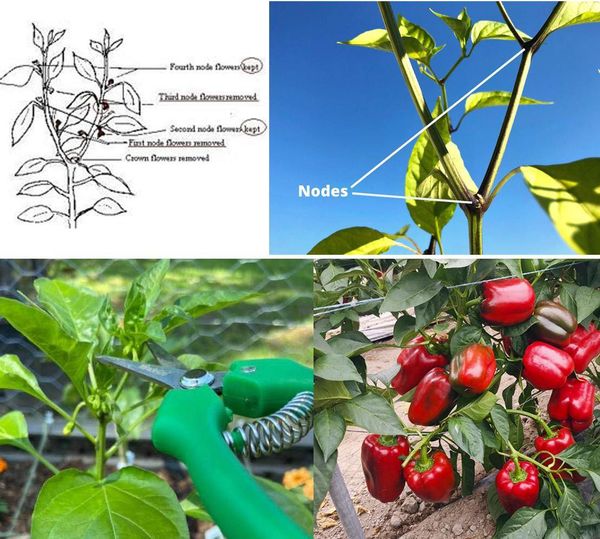
- Remove Early Flowers: Pinch off early flowers when the plant is young to focus on root and foliage development.
- Top the Plant: At 6-8 inches tall, pinch or cut off the topmost growing tip to encourage bushier growth.
3. Mid-Season Pruning
- Identify Suckers: Remove small shoots growing in the junction between the main stem and branches to prevent overcrowding and improve airflow.
- Thin Out Foliage: Remove leaves touching the ground or crowding the center to reduce disease risk and enhance sunlight penetration.
- Prune Damaged or Diseased Branches: Regularly inspect and remove any damaged or diseased branches to maintain plant health.
4. Late-Season Pruning
- Top Off the Plants: Cut off the topmost growth about a month before the first frost to focus on ripening existing fruits.
- Remove Remaining Flowers: If there are still flowers or undeveloped fruits, remove them to help the remaining peppers mature.
Additional Tips for Pruning Pepper Plants
1. Consistent Pruning
- Approach: Perform regular, light pruning rather than heavy cuts to avoid stressing the plant. Consistent pruning encourages steady growth.
2. Fertilization
- Post-Pruning Care: Use a balanced fertilizer after pruning to support overall plant health. Opt for equal parts nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Organic options like compost or fish emulsion are effective.
3. Watering
- Routine: Maintain consistent watering to support strong root development and fruit production. Avoid overhead watering to minimize fungal diseases, and consider drip irrigation or soaker hoses.
4. Pest Management
- Monitoring: Regularly check for pests like aphids, spider mites, and caterpillars. Use organic pest control methods such as neem oil or insecticidal soap, and introduce beneficial insects as needed.
5. Mulching
- Purpose: Apply mulch around the base of your plants to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Organic mulches, like straw or grass clippings, can also enrich the soil.
6. Supporting the Plants
- Support: Use stakes, cages, or trellises to support pepper plants and prevent branch breakage under the weight of the fruit.
Pruning pepper plants is essential for maximizing their health and yield. By understanding the right timing and techniques for pruning, you can ensure your plants remain productive and healthy throughout the growing season. For more expert advice and gardening tips, explore how to grow bell peppers upside down and learn about growing jalapeno peppers without soil. Happy gardening!
For further resources, consider consulting gardening books, university agricultural extensions, and reputable gardening websites for tailored advice based on your specific conditions and pepper varieties.